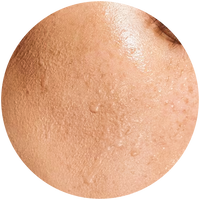
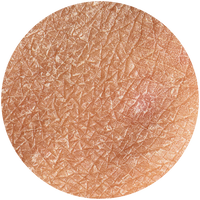
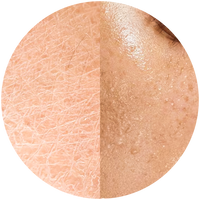
Barrier Repair & Restore Moisturiser
Sale price₹ 1,899
Gentle Hydrating Creamy Face Wash
Sale price₹ 426
Regular price₹ 449
Brightening & Exfoliating Vitamin C Daily Face Wash
Sale price₹ 474
Regular price₹ 499
Acne & Oil Control Intense Serum with 2% Salicylic Acid
Sale price₹ 524
Regular price₹ 749
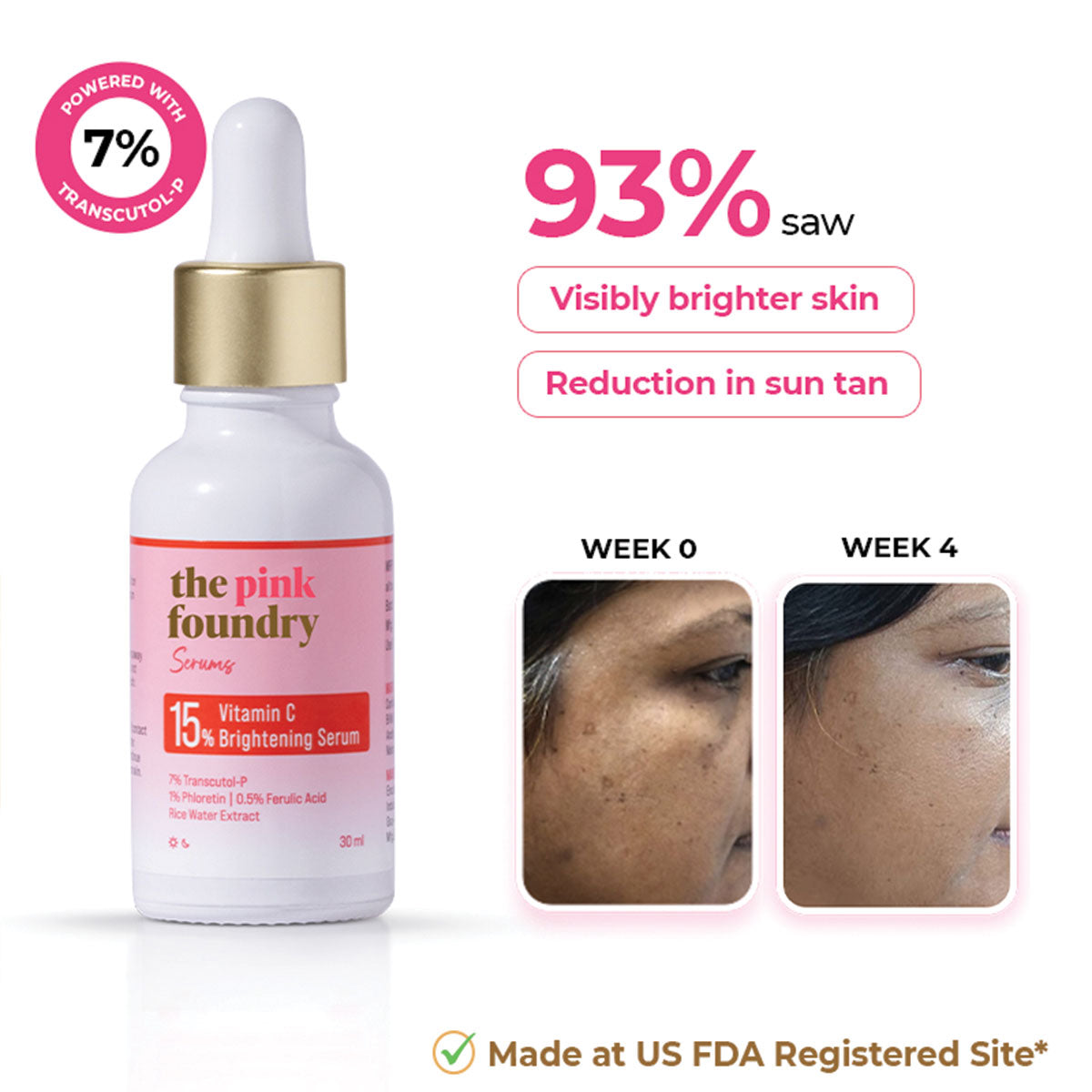
15% Vitamin C Brightening Serum
Sale price₹ 759
Regular price₹ 799
Dewy Hydrating Hybrid Sunscreen SPF 50+
Sale price₹ 749
Mini Waterlight Gel Moisturiser 72 hour Hydration
Sale price₹ 299
Mini Clearing & Calming Acne Face Wash
Sale price₹ 199
Overnight Acne Spot Corrector
Sale priceFrom ₹ 521
Regular price₹ 549
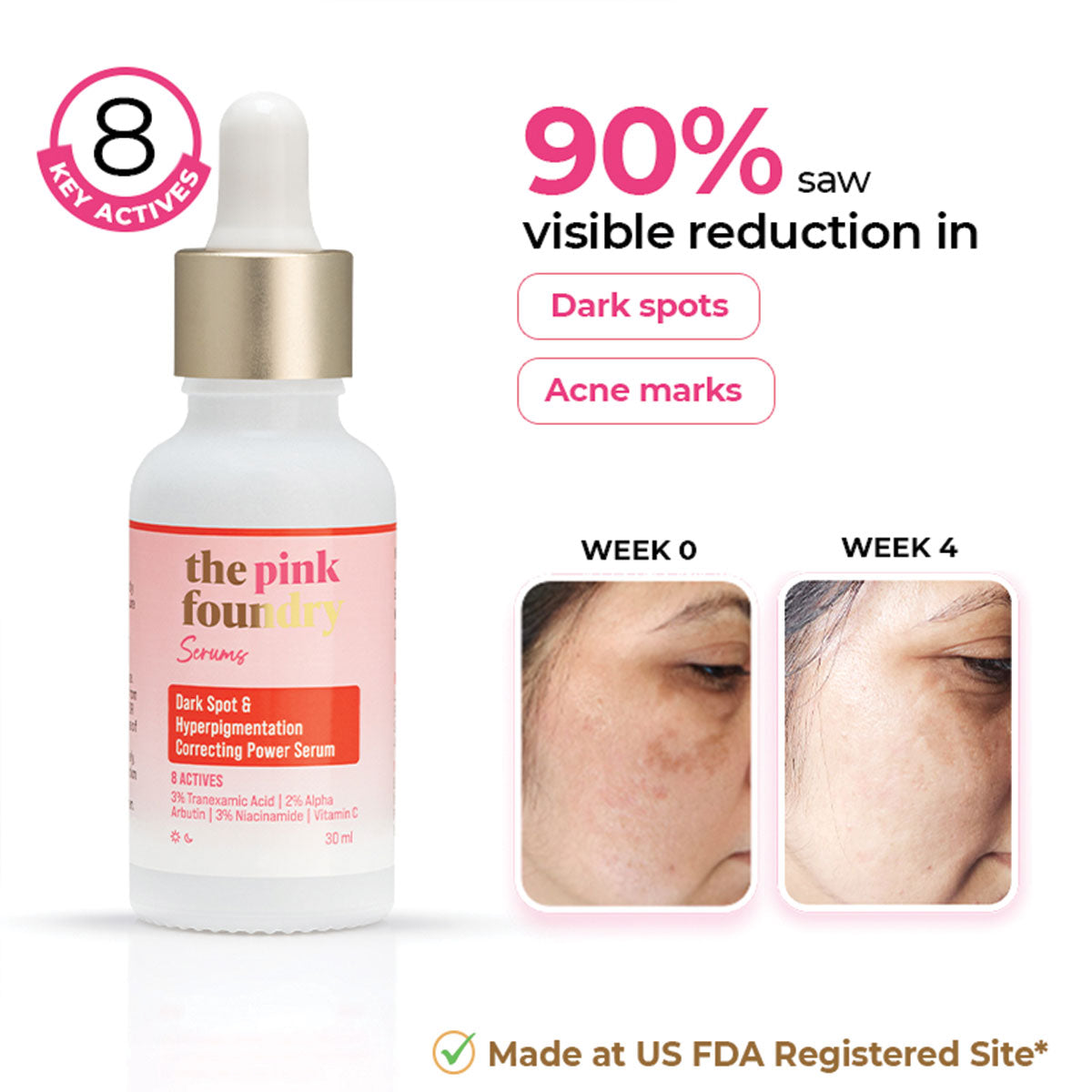
Dark Spot & Hyperpigmentation Correcting Power Serum
Sale price₹ 806
Regular price₹ 849
Acne Care & Healing Gel Moisturiser
Sale price₹ 474
Regular price₹ 499
Clearing & Calming Acne Face Wash
Sale price₹ 379
Regular price₹ 399
Brightening & Exfoliating Vitamin C Daily Face Wash
Sale price₹ 474
Regular price₹ 499
Barrier Repair & Restore Moisturiser
Sale price₹ 1,899
Shop by Skin Concern

Dark Spot & Hyperpigmentation Correcting Power Serum
Sale price₹ 806
Regular price₹ 849
15% Vitamin C Brightening Serum
Sale price₹ 759
Regular price₹ 799

Overnight Acne Spot Corrector
Sale priceFrom ₹ 521
Regular price₹ 549
Acne Care & Healing Gel Moisturiser
Sale price₹ 474
Regular price₹ 499
Clearing & Calming Acne Face Wash
Sale price₹ 379
Regular price₹ 399
Acne & Oil Control Intense Serum with 2% Salicylic Acid
Sale price₹ 524
Regular price₹ 749

Waterlight Gel Moisturiser 72 Hour Hydration
Sale price₹ 521
Regular price₹ 549
Dewy Hydrating Hybrid Sunscreen SPF 50+
Sale price₹ 749

Super Clarifying 12% Niacinamide Face Serum
Sale price₹ 711
Regular price₹ 749
Pore Refining & Soothing Clay Mask
Sale price₹ 711
Regular price₹ 749

Dark Spot & Hyperpigmentation Correcting Power Serum
Sale price₹ 806
Regular price₹ 849
15% Vitamin C Brightening Serum
Sale price₹ 759
Regular price₹ 799

Overnight Acne Spot Corrector
Sale priceFrom ₹ 521
Regular price₹ 549
Acne Care & Healing Gel Moisturiser
Sale price₹ 474
Regular price₹ 499
Clearing & Calming Acne Face Wash
Sale price₹ 379
Regular price₹ 399
Acne & Oil Control Intense Serum with 2% Salicylic Acid
Sale price₹ 524
Regular price₹ 749

Waterlight Gel Moisturiser 72 Hour Hydration
Sale price₹ 521
Regular price₹ 549
Dewy Hydrating Hybrid Sunscreen SPF 50+
Sale price₹ 749

Super Clarifying 12% Niacinamide Face Serum
Sale price₹ 711
Regular price₹ 749
Pore Refining & Soothing Clay Mask
Sale price₹ 711
Regular price₹ 749
Testimonials from